Chapter 7 :Dynamics
Thursday, 29 September 2011
Chapter 8 Support and movement
Unit 8.2 Support systems in Plants
1. Plants on land can be divided into
a) woody plants
b) herbaceous plants (non-woody plants)
2. Woody plants with a single thick stem are called trees. Examples of trees are mango trees and angsana trees.
3. Woody plants with many branches close to the ground are called shrubs. Examples of shrubs are hibiscus shrubs and rose shrubs.
4. Cells of non-woody plants absorb and retain water in their cells making them firm and turgid.
Table 8.1 : Comparison of the support systems in herbaceous and woody plants
5. Some plants develop special structures to give additional support or to climb other supports toget sunlight for photosynthesis.
6. Aquatic plants cannot stay upright on land because their stems are non-woody and soft.
Water hyacinth

7. Aquatic plants can stay upright in water because their weighs are supported by the buoyancy of water
8. Some aquatic plants have many air sacs (kantung udara) in their stems and leaves. These structures make them light so that they can float on water. Examples : Lotus, water hyacinth, water lettuce, elodea and hydrilla.
9. Some aquatic plants that float on water have tiny leaves to ensure that they are not disrupted by the flow of water. Examples : Hydrilla and elodea.
1. Plants on land can be divided into
a) woody plants
b) herbaceous plants (non-woody plants)
2. Woody plants with a single thick stem are called trees. Examples of trees are mango trees and angsana trees.
3. Woody plants with many branches close to the ground are called shrubs. Examples of shrubs are hibiscus shrubs and rose shrubs.
4. Cells of non-woody plants absorb and retain water in their cells making them firm and turgid.
Features | Herbaceous | Woody |
Structure of stem | -Rings of hard woody tissue with compact secondary xylem cells | |
Support | -Supported by the turgidity of cells. -Cannot support a heavy weight. | -Supported by woody tissues. -Can support a heavy weight. |
Examples | Balsam plant, spinach | Durian tree, angsana tree |
Table 8.1 : Comparison of the support systems in herbaceous and woody plants
5. Some plants develop special structures to give additional support or to climb other supports toget sunlight for photosynthesis.
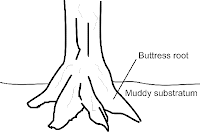
Buttress root · Thick support roots that grow from the stem above the ground · These roots hold tree firmly to the ground, giving it extra support · Examples : Angsana tree, casuarinas tree, durian tree | Prop roots · Roots which grow from the stem or branches into the ground to support the plant · Examples : Banyan tree, pandan plant maize plant | Prickles · An outgrowth of the epidermis and can be easily removed from the stem · Examples : Rose shrub | Tendrils · Curly string-like structure modified from stems and leaves · Curl and twine round parts of other plants or object to help the plant to climb · Examples : Cucumber plant, bitter gourd plant, pumpkin plant |
Thorns · Sharp modified branches that cannot be easily removed · Act as hooks to hold to supports · Examples : Bougainvillea shrub | Clasping roots · Roots that grip onto other plants or structures to get support · Examples : Money-plant, betel vine (sirih) | Stilt roots · Roots that develop from the main stem and grow into the ground for support · Examples : Mangrove tree |
6. Aquatic plants cannot stay upright on land because their stems are non-woody and soft.
Water hyacinth
Water lettuce

Hydrilla
8. Some aquatic plants have many air sacs (kantung udara) in their stems and leaves. These structures make them light so that they can float on water. Examples : Lotus, water hyacinth, water lettuce, elodea and hydrilla.
9. Some aquatic plants that float on water have tiny leaves to ensure that they are not disrupted by the flow of water. Examples : Hydrilla and elodea.
Preview
Preview










0 comments:
Post a Comment